WTF zkSync极简入门: 5. 合约开发
这个系列教程帮助开发者入门 zkSync 开发。
所有代码和教程开源在 github: github.com/WTFAcademy/WTF-zkSync
这一讲,我们将介绍 zkSync 合约开发,并实现一个自定义的 Paymaster Contract 和一个 ERC20 Contract,而且允许用户使用 ERC20 进行 gas 支付。
1.背景知识:
2. ETH 和 zkSync 的不同
zkSync Era 可以处理绝大多数基于以太坊虚拟机(EVM)的智能合约,并维持高安全标准,从而减少了重复进行安全审计的需求。但是,仍存在一定差异,必要情况下还请阅读 差异文档。
3. 实现一个 Paymaster 合约
3.1 IPaymaster 接口定义
实现该合约之前,我们先了解下 IPaymaster 接口,该接口定义如下:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.20;
import "../libraries/TransactionHelper.sol";
enum ExecutionResult {
Revert,
Success
}
bytes4 constant PAYMASTER_VALIDATION_SUCCESS_MAGIC = IPaymaster.validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction.selector;
interface IPaymaster {
/// @dev 该函数有只能由 bootloader 调用用来验证该 paymaster 实现是否同意支付交易的费用,如果付款人愿意为交易付款,则此方法必须至少发送 tx.gasprice * tx.gasLimit 给 operator
/// @param _txHash 交易的哈希值
/// @param _suggestedSignedHash 由 EOA 签名的交易哈希值
/// @param _transaction 交易本身
/// @return magic 如果 paymaster 同意支付交易费用,则返回值应等于 validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction 方法的签名。
/// @return context 交易的“上下文”:长度最多为 1024 字节的字节数组,将传递给账户的 postTransaction 方法。
/// @dev 开发者应尽量保留尽可能多的步骤,无论交易是否有效,因为这个方法也用于 gas 费用估算(不包括一些必要的数据,例如签名)。
function validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction(
bytes32 _txHash,
bytes32 _suggestedSignedHash,
Transaction calldata _transaction
) external payable returns (bytes4 magic, bytes memory context);
/// @dev 在交易执行后由 bootloader 调用。
/// @param _context, 执行的“上下文”,由 "validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction" 方法返回。
/// @param _transaction, 用户的交易
/// @param _txResult, 交易执行结果(成功或失败)。
/// @param _maxRefundedGas, 可退还给 paymaster 的 gas 上限。
/// @dev 实际退还的金额取决于“postOp”本身消耗的燃气量,因此开发人员应考虑这一点。
function postTransaction(
bytes calldata _context,
Transaction calldata _transaction,
bytes32 _txHash,
bytes32 _suggestedSignedHash,
ExecutionResult _txResult,
uint256 _maxRefundedGas
) external payable;
}
但有一点需要注意的是 postTransaction 是可选的,在交易执行后调用。请注意,与 EIP4337 不同的是,不能保证会调用此方法。特别是,如果交易因 out of gas 错误而失败,则不会调用此方法。
3.2 Paymaster 合约实现
整体合约框架如下:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import {IPaymaster, ExecutionResult, PAYMASTER_VALIDATION_SUCCESS_MAGIC} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/interfaces/IPaymaster.sol";
import {IPaymasterFlow} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/interfaces/IPaymasterFlow.sol";
import {TransactionHelper, Transaction} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/libraries/TransactionHelper.sol";
import "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/Constants.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
contract ApprovalPaymaster is IPaymaster, Ownable {
uint256 constant PRICE_FOR_PAYING_FEES = 1;
address public allowedToken;
modifier onlyBootloader() {
require(
msg.sender == BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS,
"Only bootloader can call this method"
);
_;
}
constructor(address _erc20) {
allowedToken = _erc20;
}
function validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction(
bytes32,
bytes32,
Transaction calldata _transaction
)
external
payable
onlyBootloader
returns (bytes4 magic, bytes memory context)
{
// 待实现
}
function postTransaction(
bytes calldata _context,
Transaction calldata _transaction,
bytes32,
bytes32,
ExecutionResult _txResult,
uint256 _maxRefundedGas
) external payable override onlyBootloader {
// 可选函数 这里不进行实现
}
receive() external payable {}
}
其中定义的 onlyBootloader 确保了 validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction 和 postTransaction 函数仅 BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS 可以调用。
这里的核心实现是 validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction 函数,我们依次进行解读:
magic = PAYMASTER_VALIDATION_SUCCESS_MAGIC;
require(
_transaction.paymasterInput.length >= 4,
"The standard paymaster input must be at least 4 bytes long"
);
bytes4 paymasterInputSelector = bytes4(
_transaction.paymasterInput[0:4]
);
if (paymasterInputSelector == IPaymasterFlow.approvalBased.selector) {
// 待实现
} else {
revert("Unsupported paymaster flow");
}
// Encoding the "ApprovalBased" paymaster flow's input
const paymasterParams = utils.getPaymasterParams(PAYMASTER_ADDRESS, {
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_ADDRESS,
// set minimalAllowance as we defined in the paymaster contract
minimalAllowance: BigInt("1"),
// empty bytes as testnet paymaster does not use innerInput
innerInput: new Uint8Array(),
});
这里我们验证了 paymasterInput 是否支持支付交易的费用,否则直接 revert 了整个输出,为了方便理解这里把 js 对 ApprovalBased 付款流程进行编码的代码贴了出来。
(address token, uint256 amount, bytes memory data) = abi.decode(
_transaction.paymasterInput[4:],
(address, uint256, bytes)
);
// 校验token是否是同一个
require(token == allowedToken, "Invalid token");
// 我们验证用户是否提供了足够的授权额度
address userAddress = address(uint160(_transaction.from));
address thisAddress = address(this);
uint256 providedAllowance = IERC20(token).allowance(
userAddress,
thisAddress
);
require(
providedAllowance >= PRICE_FOR_PAYING_FEES,
"Min allowance too low"
);
这里主要做的事情是校验授权的 token 额度是否足够,实际的开发过程中其实是需要根据实际的 gas 反推出需要授权额度的,这里为了简单这我们在合约中写死了固定的 1。
uint256 requiredETH = _transaction.gasLimit *
_transaction.maxFeePerGas;
try
IERC20(token).transferFrom(userAddress, thisAddress, amount)
{} catch (bytes memory revertReason) {
if (revertReason.length <= 4) {
revert("Failed to transferFrom from users' account");
} else {
assembly {
revert(add(0x20, revertReason), mload(revertReason))
}
}
}
(bool success, ) = payable(BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS).call{
value: requiredETH
}("");
require(
success,
"Failed to transfer tx fee to the bootloader. Paymaster balance might not be enough."
);
这里主要做的事情是:
计算出实际需要的 gas 费用,并将 ETH 其转到 BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS 地址,同时将用户的 erc20 转移到当前合约地址,官方的例子中这里 amount 并没有做任何的限制,但实际应该需要和当前价格进行计算得出的,给出的一个 demo 示例如下,这里的价格可以通过预言机的方式进行获取:
uint256 requiredERC20 = (requiredETH * ETHUSDCPrice)/TokenUSDPrice;
require(
providedAllowance >= requiredERC20,
"Min paying allowance too low"
);
require(
requiredERC20 >= amount,
"Not the required amount of tokens sent"
);
最后我们还需要实现一个提取和接收 ETH 的函数,因为我们可能需要将合约地址的 ETH 提取出来,代码示例如下:
function withdraw(address _to) external onlyOwner {
(bool success, ) = payable(_to).call{value: address(this).balance}("");
require(success, "Failed to withdraw funds from paymaster.");
}
receive() external payable {}
完整的代码实现如下:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import {IPaymaster, ExecutionResult, PAYMASTER_VALIDATION_SUCCESS_MAGIC} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/interfaces/IPaymaster.sol";
import {IPaymasterFlow} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/interfaces/IPaymasterFlow.sol";
import {TransactionHelper, Transaction} from "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/libraries/TransactionHelper.sol";
import "@matterlabs/zksync-contracts/l2/system-contracts/Constants.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
/// @author Matter Labs
/// @notice This smart contract pays the gas fees for accounts with balance of a specific ERC20 token. It makes use of the approval-based flow paymaster.
contract ApprovalPaymaster is IPaymaster, Ownable {
uint256 constant PRICE_FOR_PAYING_FEES = 1;
address public allowedToken;
modifier onlyBootloader() { // 可以在 validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction 函数使用该修饰符限制仅 [bootloader](https://docs.zksync.io/build/developer-reference/system-contracts.html#bootloader) 可调用
require(
msg.sender == BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS,
"Only bootloader can call this method"
);
_;
}
constructor(address _erc20) {
allowedToken = _erc20;
}
function validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction(
bytes32,
bytes32,
Transaction calldata _transaction
)
external
payable
onlyBootloader
returns (bytes4 magic, bytes memory context)
{
// By default we consider the transaction as accepted.
magic = PAYMASTER_VALIDATION_SUCCESS_MAGIC;
require(
_transaction.paymasterInput.length >= 4,
"The standard paymaster input must be at least 4 bytes long"
);
bytes4 paymasterInputSelector = bytes4(
_transaction.paymasterInput[0:4]
);
// Approval based flow
if (paymasterInputSelector == IPaymasterFlow.approvalBased.selector) {
// While the transaction data consists of address, uint256 and bytes data,
// the data is not needed for this paymaster
(address token, uint256 amount, bytes memory data) = abi.decode(
_transaction.paymasterInput[4:],
(address, uint256, bytes)
);
// 校验token是否是同一个
require(token == allowedToken, "Invalid token");
// 我们验证用户是否提供了足够的授权额度
address userAddress = address(uint160(_transaction.from));
address thisAddress = address(this);
uint256 providedAllowance = IERC20(token).allowance(
userAddress,
thisAddress
);
require(
providedAllowance >= PRICE_FOR_PAYING_FEES,
"Min allowance too low"
);
// Note, that while the minimal amount of ETH needed is tx.gasPrice * tx.gasLimit,
// neither paymaster nor account are allowed to access this context variable.
uint256 requiredETH = _transaction.gasLimit *
_transaction.maxFeePerGas;
try
IERC20(token).transferFrom(userAddress, thisAddress, amount)
{} catch (bytes memory revertReason) {
// If the revert reason is empty or represented by just a function selector,
// we replace the error with a more user-friendly message
if (revertReason.length <= 4) {
revert("Failed to transferFrom from users' account");
} else {
assembly {
revert(add(0x20, revertReason), mload(revertReason))
}
}
}
// The bootloader never returns any data, so it can safely be ignored here.
(bool success, ) = payable(BOOTLOADER_FORMAL_ADDRESS).call{
value: requiredETH
}("");
require(
success,
"Failed to transfer tx fee to the bootloader. Paymaster balance might not be enough."
);
} else {
revert("Unsupported paymaster flow");
}
}
function postTransaction(
bytes calldata _context,
Transaction calldata _transaction,
bytes32,
bytes32,
ExecutionResult _txResult,
uint256 _maxRefundedGas
) external payable override onlyBootloader {}
function withdraw(address _to) external onlyOwner {
(bool success, ) = payable(_to).call{value: address(this).balance}("");
require(success, "Failed to withdraw funds from paymaster.");
}
receive() external payable {}
}
4. 创建一个 ERC20 合约
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
/**
* @dev This contract is for basic demonstration purposes only. It should not be used in production.
* It is for the convenience of the ERC20fixedPaymaster.sol contract and its corresponding test file.
*/
contract MyERC20 is ERC20 {
uint8 private _decimals;
constructor(
string memory name,
string memory symbol,
uint8 decimals_
) payable ERC20(name, symbol) {
_decimals = decimals_;
}
function mint(address _to, uint256 _amount) public returns (bool) {
_mint(_to, _amount);
return true;
}
function decimals() public view override returns (uint8) {
return _decimals;
}
function burn(address from, uint256 amount) public {
_burn(from, amount);
}
}
5.合约部署
这里使用了 Atlas 进行合约部署,首先将 ERC20 合约部署:
Address 0x0395...7830 | zkSync Era Block Explorer
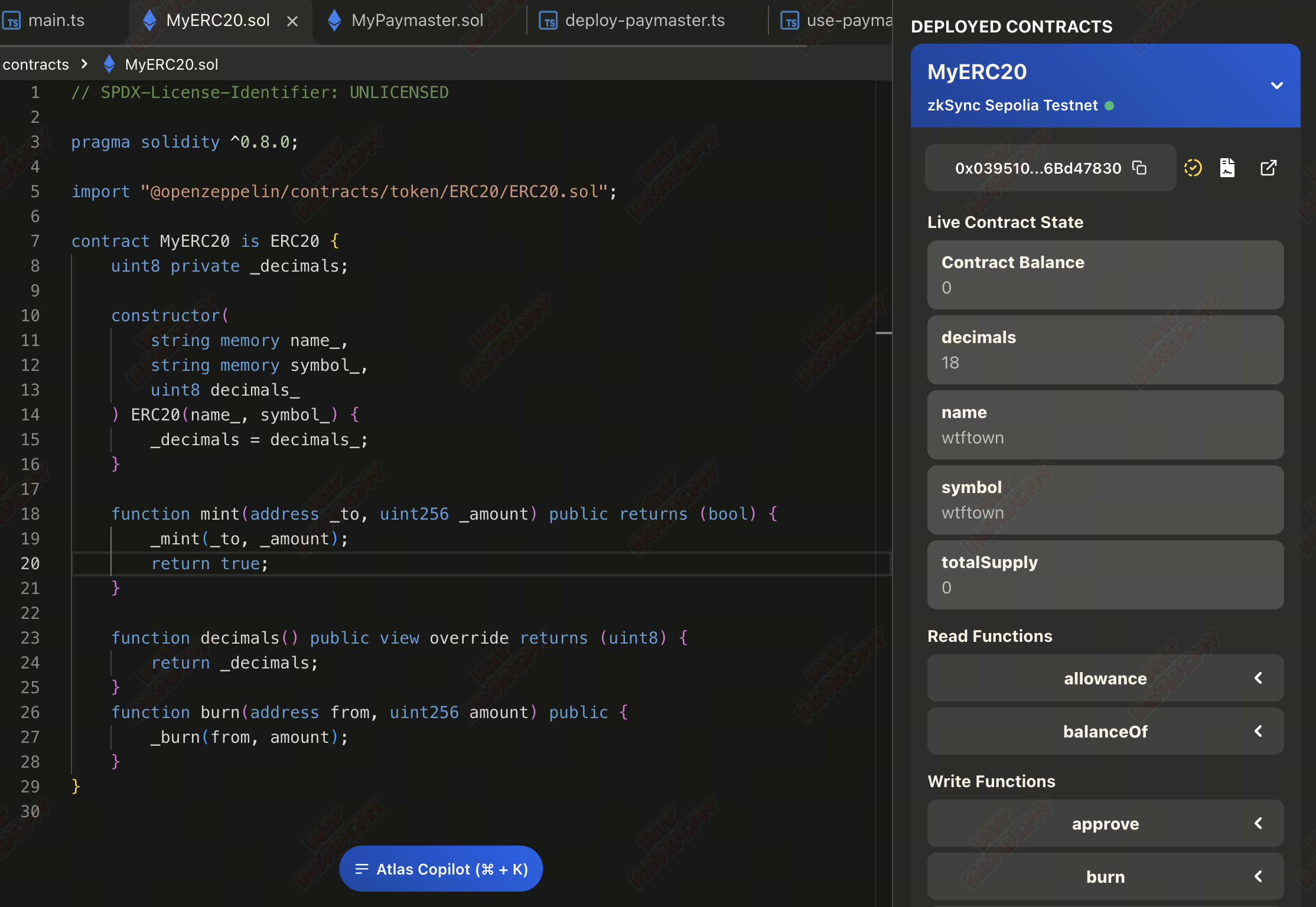
拿到 ERC20 合约地址后,再部署 MyPaymaster 合约:
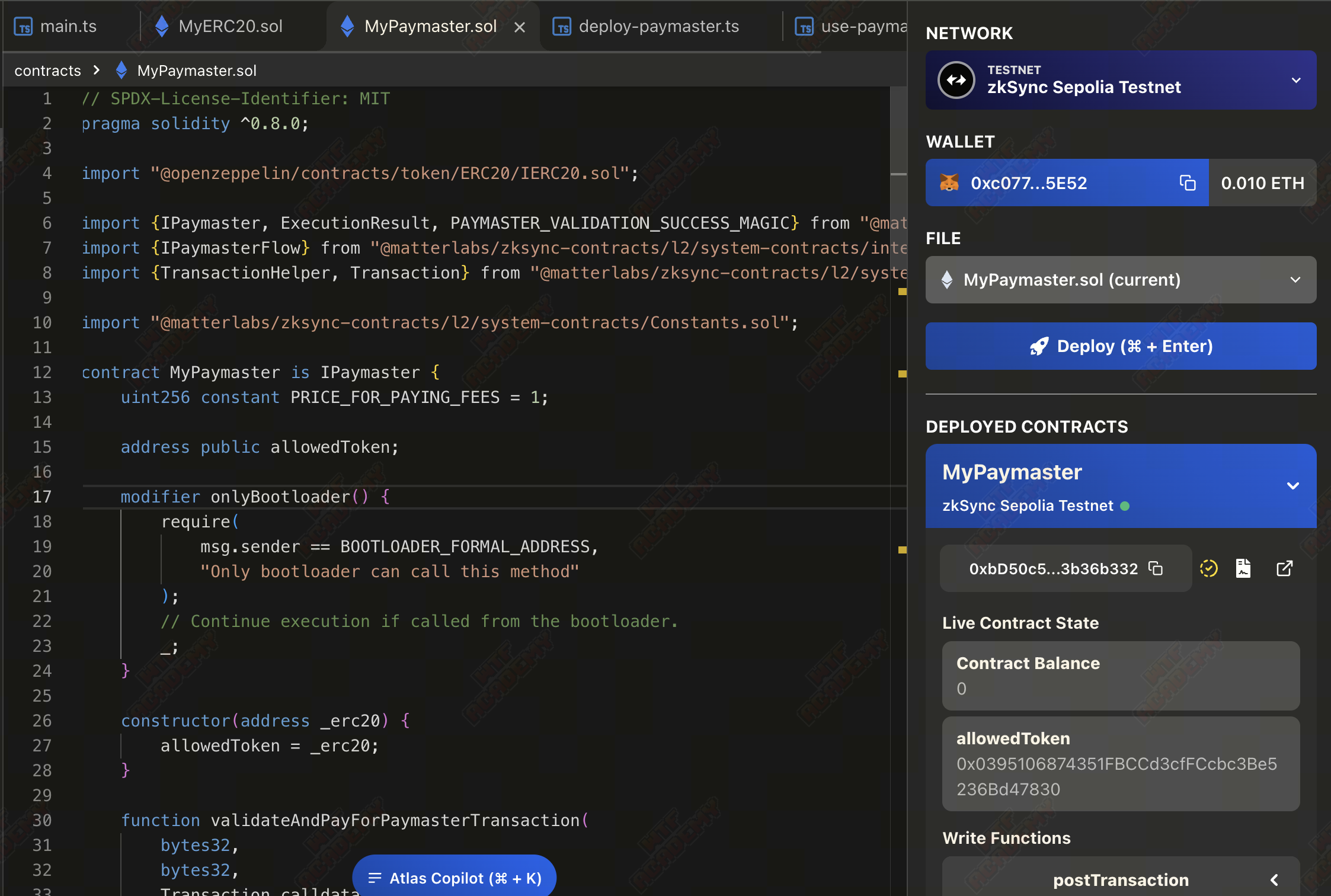
这里也可以使用脚本进行部署:
import { deployContract, getWallet, getProvider } from "./utils";
import * as ethers from "ethers";
export default async function () {
const erc20 = await deployContract("MyERC20", ["MyToken", "MyToken", 18]);
const erc20Address = await erc20.getAddress();
const paymaster = await deployContract("MyPaymaster", [erc20Address]);
const paymasterAddress = await paymaster.getAddress();
// 需要一定数量的 ETH 为 paymaster 合约提供资金,所以这里需要进行转账
console.log("Funding paymaster with ETH...");
const wallet = getWallet();
await (
await wallet.sendTransaction({
to: paymasterAddress,
value: ethers.parseEther("0.06"),
})
).wait();
const provider = getProvider();
const paymasterBalance = await provider.getBalance(paymasterAddress);
console.log(`Paymaster ETH balance is now ${paymasterBalance.toString()}`);
// Supplying the ERC20 tokens to the wallet:
// We will give the wallet 3 units of the token:
await (await erc20.mint(wallet.address, 3)).wait();
console.log("Minted 3 tokens for the wallet");
console.log(`Done!`);
}
import { utils, Wallet } from "zksync-ethers";
import { getWallet, getProvider } from "./utils";
import * as ethers from "ethers";
import { HardhatRuntimeEnvironment } from "hardhat/types";
// Put the address of the deployed paymaster here
const PAYMASTER_ADDRESS = "0x08f62b10f5C949Af8d6d8656F86A0Cc3436FB31a";
// Put the address of the ERC20 token here:
const TOKEN_ADDRESS = "0x03615ff4Af613BC55206E179dAccC5631CaA00B6";
function getToken(hre: HardhatRuntimeEnvironment, wallet: Wallet) {
const artifact = hre.artifacts.readArtifactSync("MyERC20");
return new ethers.Contract(TOKEN_ADDRESS, artifact.abi, wallet);
}
export default async function (hre: HardhatRuntimeEnvironment) {
const provider = getProvider();
const wallet = getWallet();
console.log(
`ERC20 token balance of the wallet before mint: ${await wallet.getBalance(
TOKEN_ADDRESS,
)}`,
);
let paymasterBalance = await provider.getBalance(PAYMASTER_ADDRESS);
console.log(`Paymaster ETH balance is ${paymasterBalance.toString()}`);
const erc20 = getToken(hre, wallet);
const gasPrice = await provider.getGasPrice();
// Encoding the "ApprovalBased" paymaster flow's input
const paymasterParams = utils.getPaymasterParams(PAYMASTER_ADDRESS, {
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_ADDRESS,
// set minimalAllowance as we defined in the paymaster contract
minimalAllowance: BigInt("1"),
// empty bytes as testnet paymaster does not use innerInput
innerInput: new Uint8Array(),
});
// Estimate gas fee for mint transaction
const gasLimit = await erc20.mint.estimateGas(wallet.address, 5, {
customData: {
gasPerPubdata: utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
paymasterParams: paymasterParams,
},
});
const fee = gasPrice * gasLimit;
console.log("Transaction fee estimation is :>> ", fee.toString());
console.log(`Minting 5 tokens for the wallet via paymaster...`);
await (
await erc20.mint(wallet.address, 5, {
// paymaster info
customData: {
paymasterParams: paymasterParams,
gasPerPubdata: utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
},
})
).wait();
console.log(
`Paymaster ERC20 token balance is now ${await erc20.balanceOf(
PAYMASTER_ADDRESS,
)}`,
);
paymasterBalance = await provider.getBalance(PAYMASTER_ADDRESS);
console.log(`Paymaster ETH balance is now ${paymasterBalance.toString()}`);
console.log(
`ERC20 token balance of the the wallet after mint: ${await wallet.getBalance(
TOKEN_ADDRESS,
)}`,
);
}
使用 paymaster 执行示例:
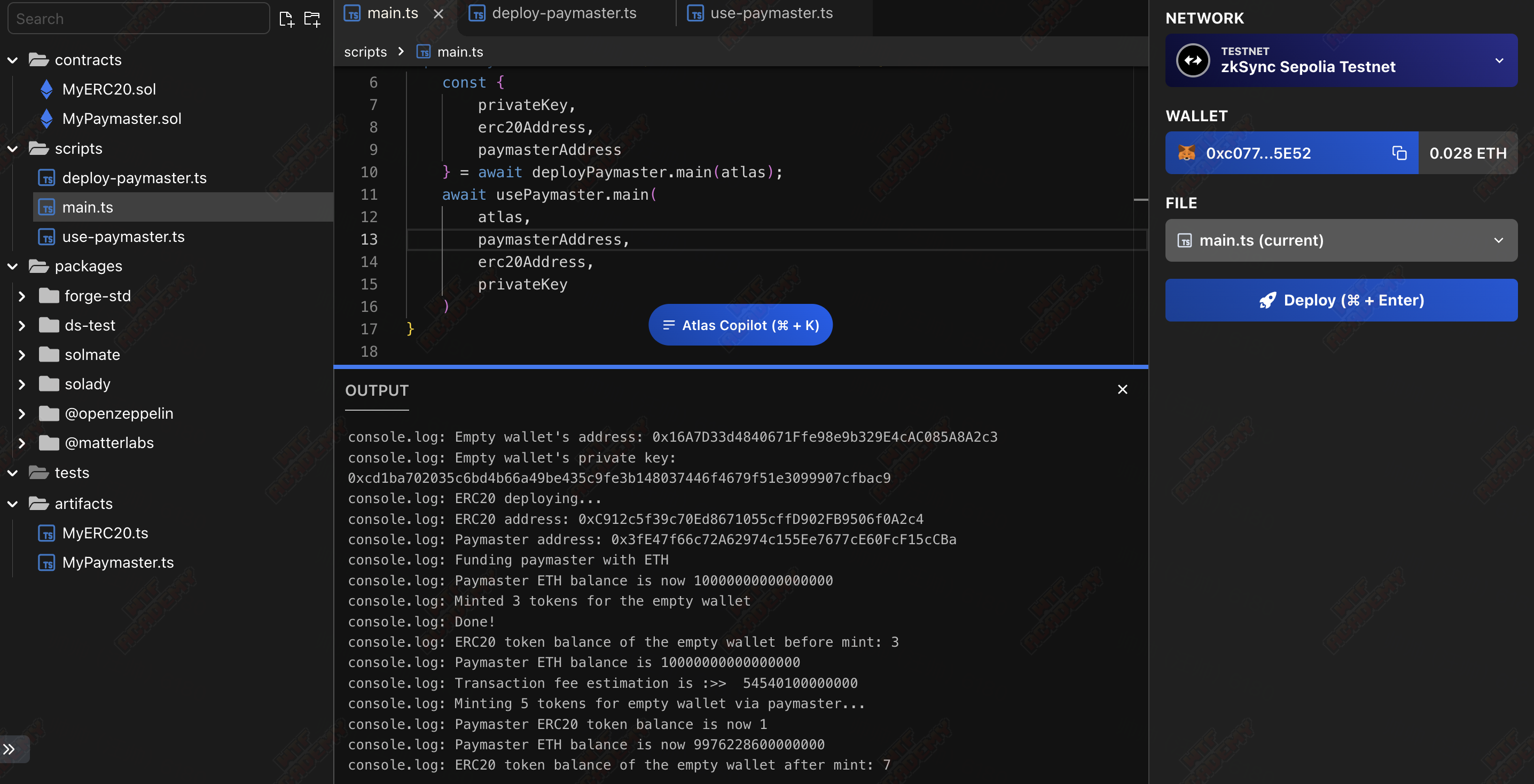
至此整个合约部分完成了,在本教程中,我们学习了如何在 zkSync Era 上设置 paymaster 合约 , 我们创建了一个 erc20,并制定了 paymaster 合约,以便它接受该代币作为费用。